How To Change Firewall Settings On Mac
While macOS offers an easy-to-apply menu for your network settings in the System Preferences menu, the Terminal app is where you need to be if you lot desire to apace wait upwards or test information almost your network configuration. Y'all tin use it to find your IP accost, detect your location, check your organisation firewall, and more.
Your network settings can be accessed using some common terminal commands that, for the almost part, require very piffling configuration to use. We notwithstanding recommend yous use the Arrangement Preferences app for configuration (unless you're happy using the terminal), but identifying your Mac terminal network settings is easy.

Using networksetup
The networksetup tool offers an enormous amount of information on your current Mac network configuration. You can use it to find your figurer name, IP address, electric current WiFi network, and more. As the name suggests, yous can also utilise it to change settings, simply we'd yet recommend using System Preferences to do this.
Yous can view a full list of potential Mac terminal network commands using the networksetup tool by typing networksetup -help at the terminal. This will display the aid list, with various examples on how to use the tool to view and modify dissimilar network settings.
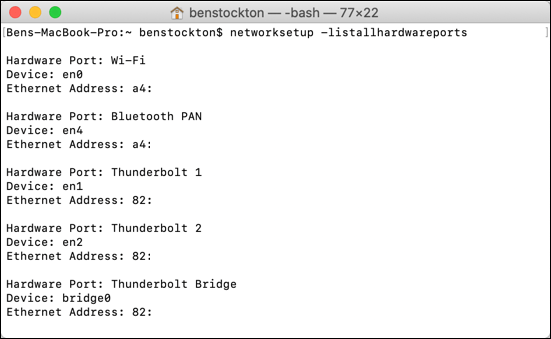
Examples of networksetup commands yous can apply to view network information include:
- To view your Mac computer proper name: networksetup -getcomputername.
- To list all Mac network connections: networksetup -listallhardwareports
- To display the current, connected WiFi network: networksetup -getairportname deviceid. Replace deviceid with a device ID from the networksetup -listallhardwareports control.
Using ipconfig
The ipconfig tool is common to Windows and macOS computers but, different the Windows version, it isn't the most useful tool for changing network settings. Where it tin exist useful, however, is listing information on your current network configuration.
Typing ipconfig at the terminal volition list all available commands, but these include:
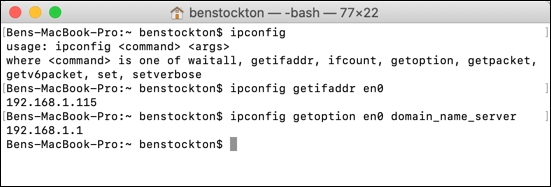
- To view your electric current network IP address: ipconfig getifaddr deviceid. Replace deviceid with the correct network device id (eg. en0). Type networksetup -listallhardwareports if y'all don't know this.
- To view your electric current network DNS server: ipconfig getoption deviceid domain_name_server (replacing deviceid with your network device id).
Using ifconfig
The ifconfig command is another network configuration tool available to users on macOS and Linux PCs. Different ipconfig, however, ifconfig is a much more powerful tool for viewing and modifying your network settings.
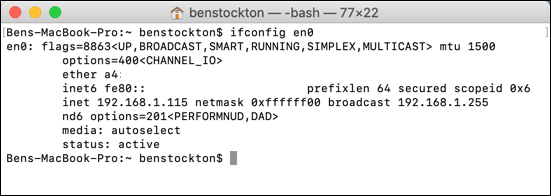
However, you merely need to type ifconfig at the terminal to view a detailed list of data for all of the network devices connected or integrated into your Mac. That includes IP and MAC addresses, electric current device status, and more.
You can view specific information by list the device id (for example, ifconfig en0) instead.
Using ping
While yous can't employ it to view any network information, yous tin use the ping command to test whether or non you can make contact with another network device. It could be a device on your network (for instance, your network router) or to a website domain or internet IP address to test your net connectivity.
Y'all'll want to employ ping as a troubleshooting tool whenever your device seems to be having issues with connecting to another device on your local network, or to a device or website the internet. It will show the time taken for information to exist sent and returned and will run continuously until yous determine to finish it.
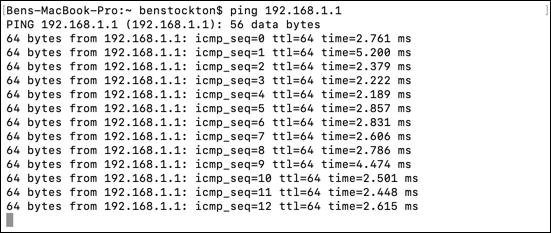
To utilise it, type ping accost, replacing accost with an IP address or domain proper name. A common target for testing is google.com—if you can't hit Google, you probably don't accept internet connectivity.
Also, ping 192.168.1.1 will test the IP accost for many local network routers (192.168.1.1).
Using netstat
The netstat tool lists information on your electric current ingoing and outgoing network connections. Any connections made to your Mac can exist listed using this tool. Windows and Linux PCs also utilize netstat, but there are some differences, with dissimilar available flags to Mac users.
There are several ways you lot tin can utilize netstat to view electric current network settings or connections. These include:
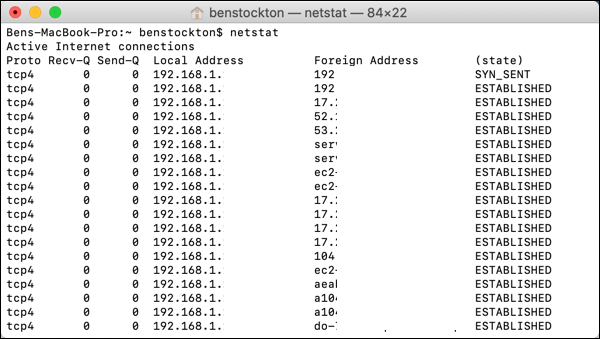
- For a current list of all agile internet connections: netstat
- To view connection data for an interface: netstat -fifty deviceid, replacing deviceid with your network interface name (eg. netstat -l en0).
- To view the IP routing table: netstat -nr or netstat -r
- To show all network statistics: netstat -s and netstat -i
For more information on how to use the netstat command and to help decipher some of the complex technical terminologies, type homo netstat to view and read through the included netstat homo page.
Using lsof
You can utilize the lsof command as a way to view whatever running processes on your Mac that take active network connections. This replaces similar functionality that you'd find with the netstat command on Windows or Linux PCs.
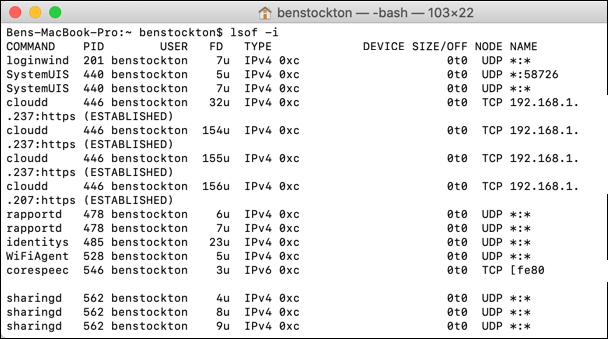
There are several ways you tin can use the lsof Mac terminal command to view network data. These include:
- To view all open network connections: lsof -i
- To view what software is using what ports: lsof -northward -i4TCP
For more than information, type human lsof to view the man page for the lsof command.
Using arp
If you desire to view a list of all active devices on a local network, you could employ the arp tool. This will listing the IP and MAC addresses for any devices that your Mac has detected on your network, based on the ARP (Accost Resolution Protocol) broadcasts those devices have made.
Typing arp -a at the terminal volition provide yous with a list of these devices.
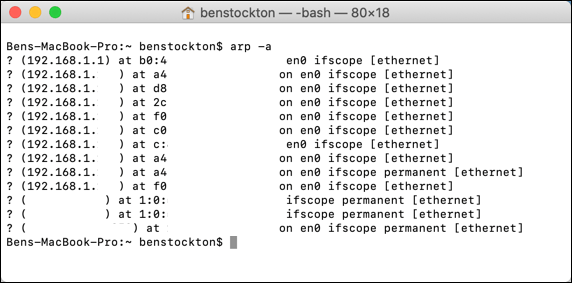
You could then combine the information constitute here with other commands like ping to determine whether or not those devices are nonetheless agile and can be communicated with from your Mac.
Configuring Your Mac Network Settings
With your Mac terminal network settings in view using these tools, you lot can identify the settings you may prefer to (or need to) alter. For case, y'all may need to spoof a MAC address on your Mac to bypass MAC address filtering on a guest WiFi network.
Information technology tin also help you identify problems, particularly if your Mac drops its WiFi connection regularly. If your Mac is having issues, apps similar OnyX for Mac tin can help yous get back upwards and running quickly.
Do not share my Personal Information.
Source: https://www.switchingtomac.com/tutorials/using-the-terminal-to-identify-network-settings/
Posted by: thorntonxvier1937.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Change Firewall Settings On Mac"
Post a Comment